The world is at better risk of infectious illnesses that originate in wildlife as a result of individuals are encroaching on tropical areas of wilderness to feed livestock and hunt wild animals.
Tropical deforestation and over-hunting are additionally on the root of global warming and mass species extinction.
Devastating pandemics like HIV/AIDS, Ebola and COVID-19 are more likely to have originated in wildlife. This serves as a reminder of how human impacts on the surroundings interlink with illness in addition to with local weather change and biodiversity loss.
Food, then, is one key to fixing plenty of issues.
We not too long ago performed a radical review of the scientific literature to discover whether or not outbreaks of infectious illnesses originating in wildlife might be linked to ecosystem degradation induced by the worldwide food system.
The evaluation revealed two methods to sort out the interrelated crises of wildlife-origin illnesses, world warming and mass species extinction. The first is a world transition to extra plant-based diets, in order to restrict agricultural encroachment on tropical wildlands. The second is to curb demand for wild meat in tropical cities.
Eating less food from livestock sources
Closer to the Equator, biodiversity turns into richer. These tropical areas have traditionally seen less growth and are significantly wealthy in wildlife and carbon shares. But in latest a long time agricultural frontiers have expanded quickly into tropical forests.
The growth of farmland into tropical forests might be rising contact between wildlife, individuals and livestock. This in flip might improve the chance of pathogens leaping from one to the opposite.
Such habitat destruction additionally has a adverse influence on massive herbivores and predators, as they lose sources of food and breeding grounds. This can result in a rise in “generalist” species of rodents, bats, birds and primates which can be higher tailored to human-modified landscapes. Some of those species are identified “reservoirs” for infectious illnesses of livestock and people. Intensive livestock farms additional improve the chance that domesticated animals grow to be intermediate hosts for wildlife-origin illnesses, usually amplifying the risk of human contagion.
In addition, if the worldwide human inhabitants continues to grow and undertake diets wealthy in livestock supply meals, it’s unlikely that world warming can be saved well below 2°C. It’s additionally unlikely that the speed of species extinction can be slowed. This is as a result of livestock manufacturing has the highest environmental footprint of all meals when it comes to land and water use, greenhouse fuel emissions and air pollution of terrestrial and aquatic techniques.
It’s not sensible or even desirable to anticipate everybody to grow to be a vegan (following a totally plant-based weight-reduction plan). But flexitarian diets might feed the rising world inhabitants with out additional increasing farmland into tropical wildlands, and with reductions in greenhouse fuel emissions. These diets consist of enormous quantities of plant-based meals (together with vegetable proteins like pulses, nuts and seeds), modest quantities of fish, poultry, eggs and dairy and small portions of crimson and processed meat.
Together with conversion to environmentally pleasant or natural farming and cutbacks in food losses and wastage, diets low in livestock supply meals are then a key element of a sustainable world food system. They produce other health benefits too, comparable to lowering weight problems, diabetes, coronary heart illness and colorectal most cancers.
Measures obtainable to governments, civil society and companies to advertise a discount within the world consumption of livestock supply meals are illustrated within the determine beneath.
Illustrator: Emily Wright, taken from Wegner et al. 2022, eClinicalMedicine
Governments are inclined to dodge such interventions for concern of public backlash. But the general public expects government leadership in tackling such a posh problem.
Curbing wild meat demand in tropical cities
In the tropical forests of Africa, Asia and South America, over the previous 30 years looking stress to provide close by cities has radically increased. High ranges of untamed meat commerce might improve the risk of disease transmission from wildlife to people, as a result of it’s exhausting for governments to implement biosecurity measures on looking grounds and at abattoirs, food markets and eating places.
Without efficient regulation enforcement and sustained shopper campaigns to scale back city demand, bans might fail to discourage commerce. In truth, customers’ sturdy preferences for wild meat imply that they could proceed to buy it regardless of value will increase induced by a ban. This would enhance black markets.
ALSO READ: Stolen police van transformed into diesel tanker by two Zim nationals
In city areas, legume, fish and livestock supply proteins are simply obtainable at inexpensive costs. But some indigenous individuals and rural communities rely on hunted meat for a significant a part of their vitamin and earnings. Outright bans would undermine their rights to hunt sustainably inside their territories.
Bans might additionally shift wild meat commerce to unlawful, unregulated channels the place less consideration is paid to biosecurity measures vital to stop contagion from wildlife-borne illnesses.
The supreme is then to comprise tropical wild meat looking and commerce by curbing demand in city areas whereas supporting looking rights and biosecurity measures amongst communities in distant subsistence areas.
Avoiding biohazards from animal supply meals
Interventions in rural communities ought to present wild meat hunters, merchants and butchers with coaching in cheap biosecurity measures they can simply undertake to keep away from an infection from contact with wild animals. Biosecurity measures must also be prolonged to livestock and wildlife farms, abattoirs, food markets and eating places, as illustrated within the determine beneath.
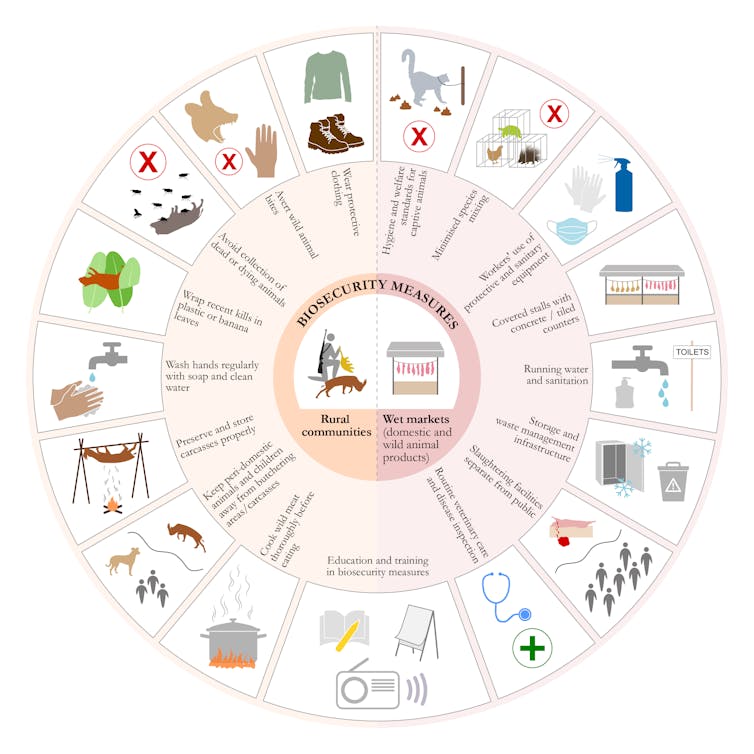
Illustrator: Emily Wright, taken from Wegner et al. 2022, eClinicalMedicine
Other bodily distancing measures must also be taken on farms, pastures and dwell animal markets. These embody fencing and lowering livestock densities to minimise contact with wild herbivores, planting fruit timber visited by bats at a distance from livestock websites, and limiting the variety of animals on sale in dwell animal markets.
Different methods throughout completely different areas
People in numerous areas depend on animals for food to different degrees. Efforts to scale back livestock manufacturing ought to deal with curbing extreme consumption in wealthier nations and the increasing metropoles of creating nations.
In the poorer rural areas of creating nations, home gardening and smallholder livestock growth programmes can assist lower malnutrition, however with less environmental influence.
People who dwell the place it’s exhausting to develop crops – comparable to pastoralists in arid rangelands and hunter-gatherers in tropical rainforests and the Arctic – will as an alternative proceed to rely conspicuously on animals for vitamin. Nonetheless, the low environmental impacts of their subsistence way of life should not similar to these of dense and higher off city populations.
Change is pressing
The incidence of infectious illnesses originating in wild animals is excessive and may be increasing. This might be yet one more signal of the best way wherein the degradation of ecosystems is undermining the capability of the planet to maintain human well being and wellbeing.
Dietary shifts away from livestock supply meals and wild meat are essential to guard the surroundings, safeguard poorer communities and cut back the risk of illness outbreaks and pandemics.![]()
Giulia Wegner, Researcher, Sustainable Development and Wildlife Conservation, University of Oxford and Kris Murray, Associate Professor, Environment and Health (MRCG@LSHTM); Senior Lecturer (Ecological Health, Imperial College London), London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine
This article is republished from The Conversation beneath a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.

