In 1800 the world’s inhabitants was round 1 billion people. Since then it has elevated eightfold to achieve 8 billion in 2022 (see determine 1), and is forecast to high 10 billion by 2050. Will inhabitants development inevitably proceed? Will it degree off over the long run? Should we attempt to cut back or cease this development?
Simply put, the world’s inhabitants is growing as a result of the variety of births outnumber deaths by two to one. A surplus of births first occurred two centuries in the past in Europe and North America, when mortality began to say no. This marked the starting of what scientists name the demographic transition. This transition subsequently unfold to the remainder of the planet as social and financial progress, mixed with advances in hygiene and drugs, started to scale back mortality charges.
Rapid inhabitants development in Africa
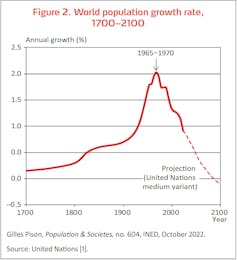
Figure 2: World inhabitants development charges, 1700-2100. Gilles Pison, based mostly on UN information, Author supplied
Still, the annual inhabitants development fee truly peaked 60 years in the past at greater than 2%, and has fallen by half since then, to 1% in 2022 (see determine 2). This development ought to proceed in coming many years as a result of fertility is reducing at international degree, from 5 youngsters per girl in 1950 to 2.3 immediately. In 2022, the areas the place fertility is (nonetheless) excessive – above 2.5 youngsters per girl – embrace virtually all of Africa, some nations of the Middle East, and part of Asia stretching from Kazakhstan to Afghanistan and Pakistan (see map under). These are the areas that can drive future world inhabitants development.
A key development in future many years will probably be inhabitants development in Africa. Including North Africa, the continent’s inhabitants may triple by the finish of the century, rising from 1.4 billion inhabitants in 2022 to three.9 billion in 2100 in line with the UN medium projection. While, globally talking, one particular person in six at the moment lives in Africa, the proportion will in all probability be greater than one in three a century from now. Growth needs to be particularly fast in sub-Saharan Africa, the place, below this identical situation, the inhabitants is set to rise from 1.2 billion in 2022 to three.4 billion in 2100.
World fertility (2022), common variety of youngsters per girl
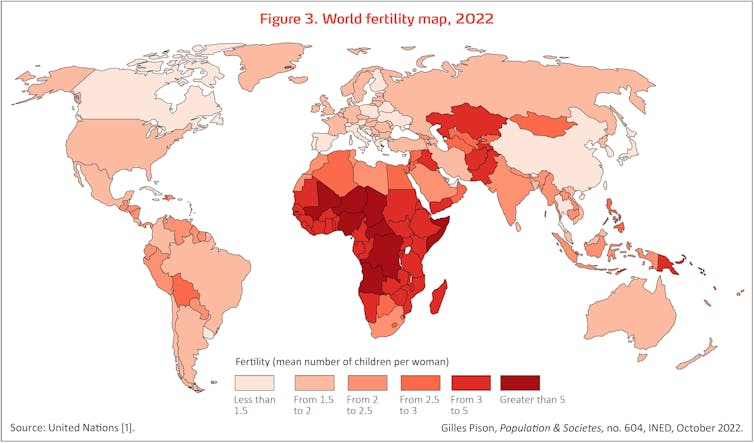
Figure 3: World fertility (2022), common variety of youngsters per girl. Gilles Pison, based mostly on UN information, Author supplied
What will occur in the coming many years?
These figures are projections, and nobody can predict what the future will deliver. That stated, demographic projections are fairly dependable for forecasting inhabitants measurement over the subsequent 10, 20 or 30 years. Most of the people who will probably be alive in 2050 have already been born, their quantity is identified and we are able to estimate fairly precisely the proportion amongst these at the moment alive who will die over the interval. Likewise, the girls who will bear youngsters over the subsequent 20 years are already alive immediately, and could be counted. By estimating their potential fertility we are able to decide the variety of future births with relative accuracy.
[Nearly 80,000 readers look to The Conversation France’s newsletter for expert insights into the world’s most pressing issues. Sign up now]
It could be unrealistic to think about that inhabitants tendencies could be modified over the quick time period. Depopulation is not an choice. Indeed, how may it probably be achieved? Through elevated mortality? No one hopes for that. Through mass migration to Mars? Unrealistic. Through a drastic and sturdy lower in fertility to under substitute degree (2.1 youngsters)? This is already happening in many elements of the world, as {couples} determine to have fewer youngsters in order to present them the finest probabilities for an extended and fulfilling life.
But for causes of demographic inertia, this doesn’t outcome in a right away inhabitants decline. Even if world fertility had been simply 1.5 youngsters per girl, as is the case in Europe, the inhabitants would proceed to extend for a number of extra many years; there are nonetheless giant numbers of adults of childbearing age who had been born when fertility was nonetheless excessive, so the variety of births additionally stays excessive. The proportion of previous and really previous people is very small at the world degree, on the different hand, so deaths are far much less quite a few.
The query of fertility decline
Demographers had been taken unexpectedly in the Nineteen Sixties and Nineteen Seventies when surveys revealed the onset of a pointy decline in fertility in many nations of Asia and Latin America, and demographic projections for these areas of the world had been revised strongly downward.
Another newer shock issues intertropical Africa. Fertility decline in the area was anticipated to start later than in Asia and Latin America due to later social and financial improvement. But it was assumed that, whereas delayed, the transition would observe the normal sample, with a decline just like that noticed in different areas of the Global South. This is certainly the case in North and southern Africa, however not in intertropical Africa, the place the decline is occurring more slowly. This explains the upward revision of projections for Africa, a continent which could possibly be house to greater than a 3rd of the world’s inhabitants by 2100.
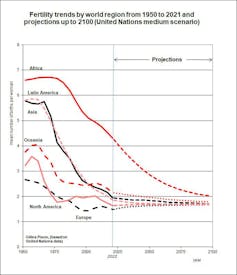
Figure 4: Fertility-rate tendencies by world area. Gilles Pison, based mostly on UN information., Author supplied
Fertility is in reality reducing in intertropical Africa, however primarily amongst the educated and concrete populations fairly than in rural areas the place most of the inhabitants nonetheless lives. While the fertility decline is nonetheless slower than that noticed some many years in the past in Asia and Latin America (see determine 4), the purpose doesn’t lie in an unwillingness to make use of contraception.
While most rural households have but to undertake a two-child household mannequin, they would like to have fewer youngsters and to house them additional aside. They are keen to make use of contraception for this function, however the obligatory companies will not be out there to them. National birth-control programmes exist however are ineffective as a result of they lack sources and, above all, as a result of their organisers and the personnel accountable for implementing them are unenthusiastic. Many will not be satisfied of the benefits of contraception, even at authorities degree, even when this is not the official line adopted with respect to worldwide organisations.
This is considered one of the variations with respect to Asia and Latin America in the Nineteen Sixties and Nineteen Seventies, and considered one of the obstacles to sooner fertility decline in sub-Saharan Africa.
Long-term outlook: explosion, implosion or equilibrium?
Beyond the subsequent 50 years, nonetheless, the future is rather more unsure and there is no established forecasting mannequin.
The demographic transition, which has served properly to foretell adjustments over the final two centuries, will probably be of little use for this distant future. There is a lot uncertainty about future fertility. If the very small household turns into a dominant mannequin over the long run, with imply fertility of fewer than two youngsters per girls, then the world inhabitants, after peaking at 10 billion, will progressively lower to the level of extinction.
But one other situation is attainable, in which fertility recovers in the nations the place it is now very low, finally stabilising at greater than two youngsters per girl worldwide. This would outcome in steady development, and once more in the extinction of the human race, this time as a result of overpopulation. If we can’t resign ourselves to those catastrophic situations of extinction by way of under- or over-population, then we should think about a situation of final equilibrium.
It is life selections that matter
Of course, people should begin considering immediately about the want for long-term equilibrium, but it surely is the subsequent few many years which might be of most pressing concern.
The world inhabitants will inevitably enhance by 2 billion between now and 2050 due to demographic inertia that nobody can forestall. Nonetheless, we now have the energy to alter our way of life – and there is an pressing want to take action – by making certain larger respect for the surroundings and extra environment friendly use of pure sources. All in all, the long-term survival of humankind relies upon extra on its selection of way of life than on its inhabitants measurement.![]()
Gilles Pison, Anthropologue et démographe, professeur au Muséum nationwide d’histoire naturelle et chercheur associé à l’INED, Muséum national d’histoire naturelle (MNHN)
This article is republished from The Conversation below a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.

